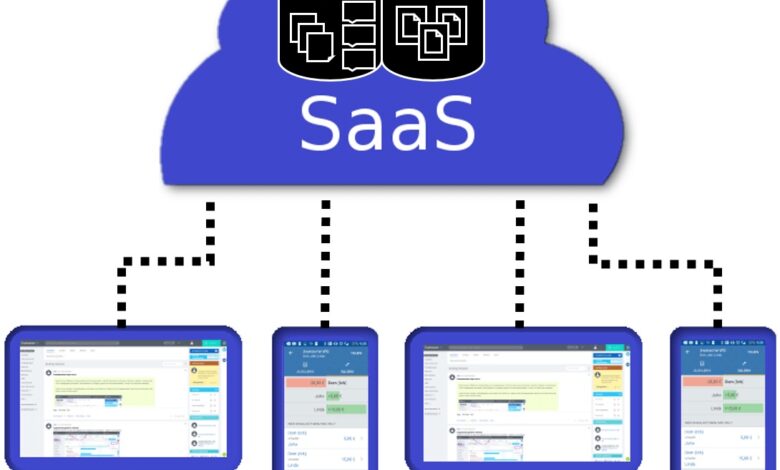
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
Software as a service (SaaS) is a method of providing software as a service through the Internet. Instead of installing and maintaining software, users just use the Internet to access it, eliminating the need for complicated software and device maintenance.
Web-based software, on-demand software, and hosted software are all terms used to describe SaaS applications. SaaS applications are hosted by Saas supplier service. The service provider is in charge of the application’s security, accessibility, and efficiency.
The Benefits of SaaS
Customers that use SaaS don’t have to buy, install, maintain, or update any hardware or software. Application access is simple: all you need is an Internet connection.
Characteristics of SaaS
To grasp the SaaS model, assume a financial institution that protects each customer’s privacy while providing secure service. Customers of a bank can utilize the same financial processes and technology without fear of unauthorized access to their personal information.
The main characteristics of the SaaS method are met by a “bank.”
Architecture for Multiple Tenants
A multitenant architecture is one in which all users and apps share a single, centrally managed infrastructure and code base. Users of Software development companies have the same network, allowing suppliers to improve faster and save production time that would be spent maintaining several variants of aged code.
Customization is simple.
Each user capacity to readily customize programs to meet their business operations without compromising the shared infrastructure. These customizations are unique to each firm or user due to the way SaaS is built, and they are always retained across updates.
The Consumer Web is Harnessed by SaaS.
The Web interface of common SaaS programs will be recognizable to anybody who has used Amazon.com or My Yahoo! You can adapt with point-and-click ease using the SaaS approach, making the weeks or months it takes to update traditional corporate software look hopelessly antiquated.
Trends in SaaS
SaaS integration platforms (or SIPs) are presently being developed by companies in order to construct more SaaS apps. The “third wave” in software adoption, according to consulting company Saugatuck Technology, occurs when SaaS advances beyond standalone program capabilities to become a platform for mission-critical applications.
Spending on SaaS vs. whole IT
Despite the fact that the pandemic had a negative impact on global organizations and economies this year, cloud growth continues to accelerate.
“While new circumstances, change system strength, support various work models, and other changing things altered by the pandemic, groups are changing their timelines on digital work initiatives and moving rapidly to the cloud,” said Brandon Medford, senior principal analyst at Gartner.
“The pandemic’s economic, organizational, and social consequences will continue to represent a spur for digitalization and cloud adoption,” said Henrique Cecci, Gartner’s senior research director. “This is certainly relevant for hybrid workforce use cases including collaboration, temporary employment, and new digital services.”
SaaS vs. other cloud services for cloud growth
The future of SaaS is undoubtedly the brightest of all cloud possibilities. After all, as more firms use SaaS solutions for a range of business operations, far beyond the early SaaS domains of core engineering and sales apps, the total growth of the SaaS market will stay stable over the next few years.
SaaS has a substantial advantage over other cloud services since it was the first to genuinely take off. According to Gartner, SaaS will remain dominant in the market far into 2022.
SaaS firms with the most revenue
The profitability of SaaS products may also be measured in terms of the firms that create them. The ten largest publicly held SaaS businesses by market valuation in the first half of 2021 were.
The most profitable SaaS companies
SaaS product profitability may also be quantified in terms of the companies that develop them. In the first half of 2021, the 10 biggest publicly owned SaaS enterprises by market capitalization were.
The increase these organizations have achieved is enormous when compared to similar data from 2020. Consider the following scenario:
- Salesforce alone increased its market capitalization from $161 billion in January 2020 to $251 billion in September 2021.
- Similarly, in early 2020, Shopify was valued at $52.1 billion, comparable to more over $185 billion today—a 225 percent increase in only 20 months!
Ms and Oracle are two notable industry heavyweights that are absent from this list. Moreover, it’s vital to remember that they make a large percentage of their money selling on-premises software, so calling them Saas applications is a misnomer.
Legacy enterprises, on the other hand, are being pushed to quickly move their software solutions to a SaaS methodology by the desire for subscription-based pricing structures.
Read Also – GitHub: Where World Builds Software
This suggests that SaaS solutions have a lot of room to expand in the coming years because their Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is comparable to on-premise software deployment strategies. As a rising number of customers may take benefit of the same product features with the possible subscription-based price model, the business software industry leaders—IBM, Oracle, Microsoft, and SAP—will likely maintain their pricing power for enterprise software applications.
Acquisitions of SaaS companies and first public offerings (IPOs)
Of course, revenue predictions aren’t the only factor in SaaS growth. Acquisitions of SaaS startups seem to be happening on a daily basis, as larger organizations search for the next great SaaS thing. Developers, inventors, and businesses have been motivated to build new SaaS solutions due to the economy’s stability and investor interest in scalable cloud solutions.
In 2021, there will be a lot of SaaS acquisitions, fueled by significant saas funding.
The following are notable SaaS purchases from the first half of 2021:
- Dropbox paid $165 million for Docsend, which enables people to exchange and track documents over a secure connection.
- The networking hardware juggernaut Kenna Security, a global leader in risk-based security solutions, was acquired by Cisco.
- ZoomInfo bought Chorus.ai, a conversations analytics provider, for $575 million in July.
- Panasonic Corporation has finalized the purchase of Blue Yonder, a leading end-to-end digital fulfillment platform supplier.
- Recent Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) in the Software as a Service (SaaS
Industry leaders have continued to rely on SaaS applications in light of recent changes in the employment landscape. Multiple SaaS businesses will be able to IPO in 2021 as a result of this surge in business. In instance, compared to the same period in 2020, the number of enterprises specializing in SaaS that have IPOed has surged by 125 percent in 2021.
The following are some of the most notable SaaS IPO stories from the last year
Couchbase
Couchbase, a NoSQL database expert, went public on July 22 and saw a price spike of 39% to $33.25 a share on the first day, valuing the firm at more than $1 billion.
Sprinklr
SentinelOne cybersecurity startup debuted on the stock market on June 30 and closed at $42.50 per share, valuing the business at $10 billion. Endpoint security is the company’s specialty, and it uses machine learning (ML) to combat cyber-attacks.
Adoption of SaaS and the size of the workforce
We may also track SaaS adoption to see if consumers are utilizing more, fewer, or the same amount of SaaS items.
In recent years, the number and types of consumers of SaaS products have exploded. Initially marketed as a solution for SMBs and startups, SaaS is now being used by businesses of all sizes as a digestible, cost-effective way to enable agility and digitalization.
The SaaS market is now increasing at an annual rate of 18%.
- By the year 2021, 99 percent of businesses will have implemented one or more SaaS solutions.
- Almost 78 percent of small enterprises have previously made a SaaS investment.
- The usage of SaaS in the healthcare business is increasing at a pace of 20% each year.
- Agility and adaptability are two of the main motivators for implementing SaaS solutions, according to 70% of CIOs.
Several variables contribute to the proportionality of SaaS adoption to workforce size:
- Small businesses often engage on a restricted number of projects, which necessitates a limited number of goods. Users working on separate projects may have their own requirements for SaaS products as the company expands and the number of teams rises.
- To minimize the costs and security risks associated with shadow IT—the use of unauthorized software at work—large enterprises make it easy to supply as many SaaS resources as needed.
- Because large-scale corporate projects are so complicated, no one SaaS solution can provide all of the required features.
- Because large-scale corporate projects are so complicated, no one SaaS solution can provide all of the required features. Users who employ numerous SaaS solutions to meet their technological needs may choose from a variety of products targeted at the same audience and application use cases.
What is the appeal of SaaS?
Despite the limited IT resources, customers are increasingly choosing the premium account pricing model to meet expanding IT demands, especially for SMBs and startups. Regardless of their size, established businesses aren’t dismissing SaaS. Instead, they’re fully embracing the as-a-service business model in order to meet a wide range of demands with flexible, contemporary solutions.
As a consequence, a favorable business climate exists, allowing for healthy competition among SaaS companies as market demand grows tremendously.
Customer advantages of SaaS
- From the standpoint of the consumer, SaaS products provide a number of advantages:
- When compared to on-premise software deployments, SaaS provides more strategic value. Secure development time has been cut from weeks and days to a few minutes because to the SaaS model.
- Users have a diversified collection of resources to satisfy a variety of requests thanks to the abundance of corporate SaaS solutions accessible. As a result of the feature-rich SaaS solutions meant to improve customer experience, enterprises are seeing increasing levels of staff engagement.
- Feature enhancements, bug fixes, and security upgrades can also be pushed out on the fly by SaaS suppliers.






