What is Structured Data for SEO And Where To Use It?
What is the definition of structured data? It is for SEO has been referenced in articles about search engine optimization (SEO), and you’ve probably seen it while viewing search results, but what is it and how does it operate on a site like yours?
The first thing that comes to mind when building a website is probably not difference and how it affects your site.
However, the method you display your knowledge is crucial. Understanding the difference and being able to use this data on your sites will help you succeed.
What is Structured Data?
Any data that is stored in a fixed field within a file is classified as structured data. It is the metadata that enables search engines understand how to read and display content in the area of SEO.
This data is a means of describing your website so that search engines can better understand it.
You’ll also need a vocabulary that delivers content in a way that search engines can understand to describe your site to search engines.
The big search engines utilize a language called Schema.org, which converts your material into code in which they can understand.
Search engines parse the code and use it to present search results in a more targeted and detailed manner. This code is simple to implement on your website.
How does Google use structured data?
To offer this information, a search engine like Google uses this data snippets and data labels that appear in your page’s HTML code.
These extra characteristics about your page help Google to adjust the appearance of search results in search engine result pages (SERPs).
You can provide users additional value when they search on Google with this data for Google.
How does structured data for SEO work?
A crawler, spider, or bot from a search engine (such as Google) must crawl and index your website in order for it to appear in search results.
When bots explore your website, they collect and index all of the information on it, from the text to the photos to the this data. The search engine then uses its algorithm to analyze the data.
Search engines continue to alter their algorithms because deciphering a website isn’t always easy. It can also help crawlers and search engines perform more efficiently.
You can also provide immediate, easy-to-understand information about your page with it. Rather than assuming what your page is about, a search engine can see if it contains:
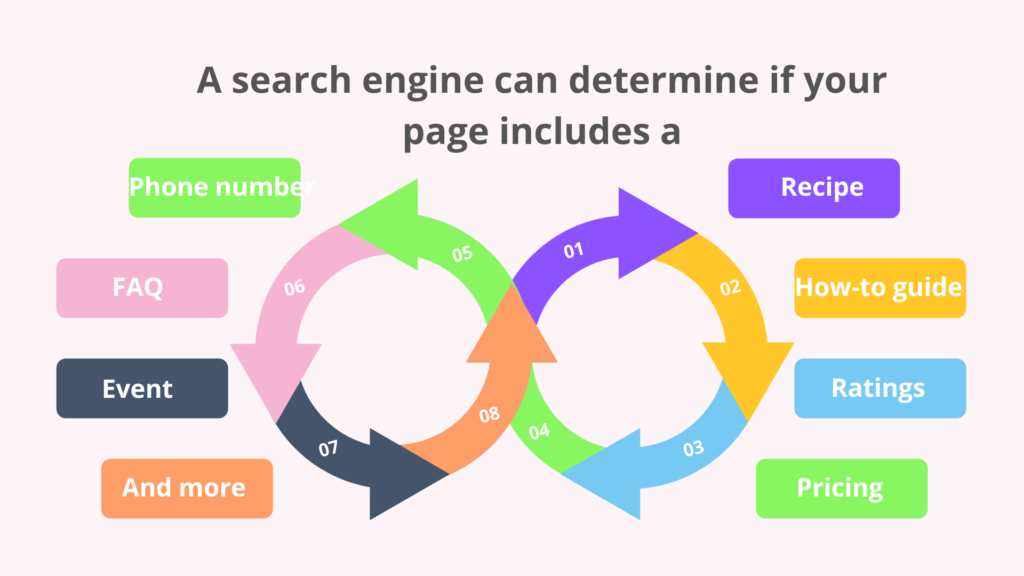
That information can subsequently be used by the search engine to streamline a user’s search. For example, if someone is seeking for a key lime pie recipe, they are likely to have a few preferences that they did not include in their initial search.
They may, for example, require a recipe that takes less than an hour to prepare. They’ll almost certainly want one that’s tasty as well! For a basic search like “key lime pie recipe,” SEO data can supply all of this information.
Read Also: What Is Google AdSense And How Does It Work?
When discussing how it works, it’s important to note that Google’s search results don’t always change.
Even if you add schema markup to a page, such as product pricing, Google may ignore it for a variety of reasons, including search intent.
Why does structured data for SEO matter?
Most businesses learn about schema markup when researching SEO. When it comes to SEO, you want to increase your search engine presence.
It’s not fun to be on the second, third, or fourth page of search results. Furthermore, 75% of consumers only look at the first page of search results.
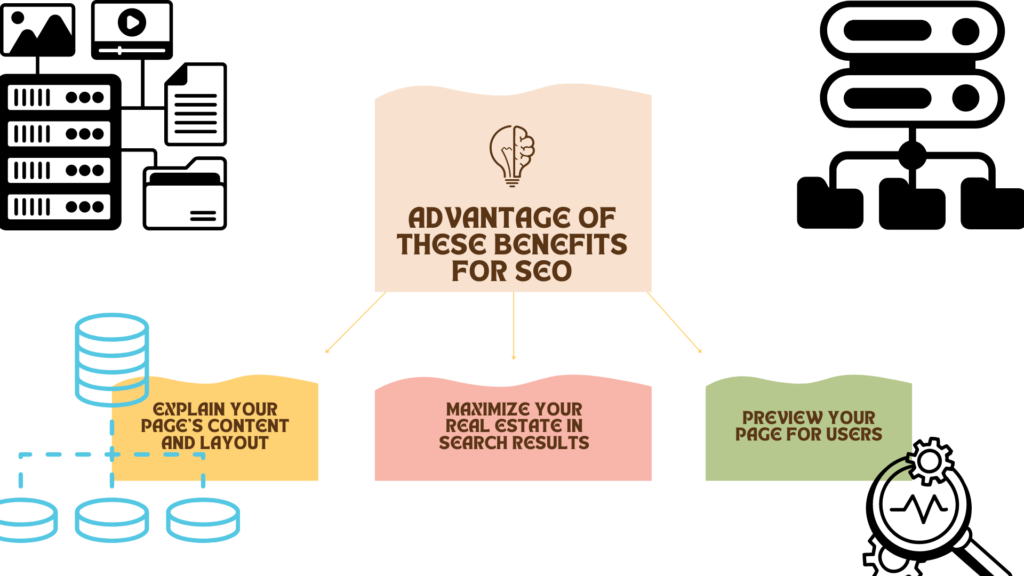
Explain your page’s content and layout
It gives Google everything it needs to understand your page. Providing Google with a detailed breakdown of your page can help you rank higher in search results.
This is because it eliminates any doubts about the format and content of your page.
Because you transcribe and translate your page using this or schema markup, Google knows what it’s about.
You can use schema markup to remove any uncertainty about your page and its purpose, whether it’s a recipe, an event, or a how-to.
Google can authenticate that your page publishes a recipe, posts an event, or provides a how-to guide, for example, by examining the content and data on your page.
Maximize your real estate in search results
While schema markup will not rocket your page to the top of search results (other off-page and on-page SEO elements will), it will provide you the opportunity to maximize your presence in search results.
By examining the impact of a featured snippet, you can see how some structured snippets, such as video, can make a difference.
You’ll see a highlighted snippet at the top of 50 percent of search results, which takes its data from one of the top-ranking websites for your search. This snippet provides a direct response to your query.
Preview your page for users
You expect quick responses whether you’re looking for an emergency plumber to fix a leaking toilet or a blog post providing lawn care suggestions.
You, like everyone else, do not want to waste their time. That’s why Google incorporates user experience into its ranking algorithm.
For several reasons, this data for Google can help your website give a better customer experience.
- You give Google a complete blueprint to your page
This template ensures that Google understands your page completely. With that amount of knowledge, Google can easily decide whether your page provides value to users, which can help it rank higher in search results.
- You provide users with a useful preview of your page
For example, a rating organized snippet might offer important trust signals about your items or services. A recipes structured sample, but at the other hand, can help users see if their meal fits their time limits and nutritional choices.
All of these data can persuade a user to redesign your site. These SEO advantages have made this data a crucial component of your SEO approach.
How to use structured data for SEO?
Are you ready to start using schema markup on your website? Begin by following these four steps:
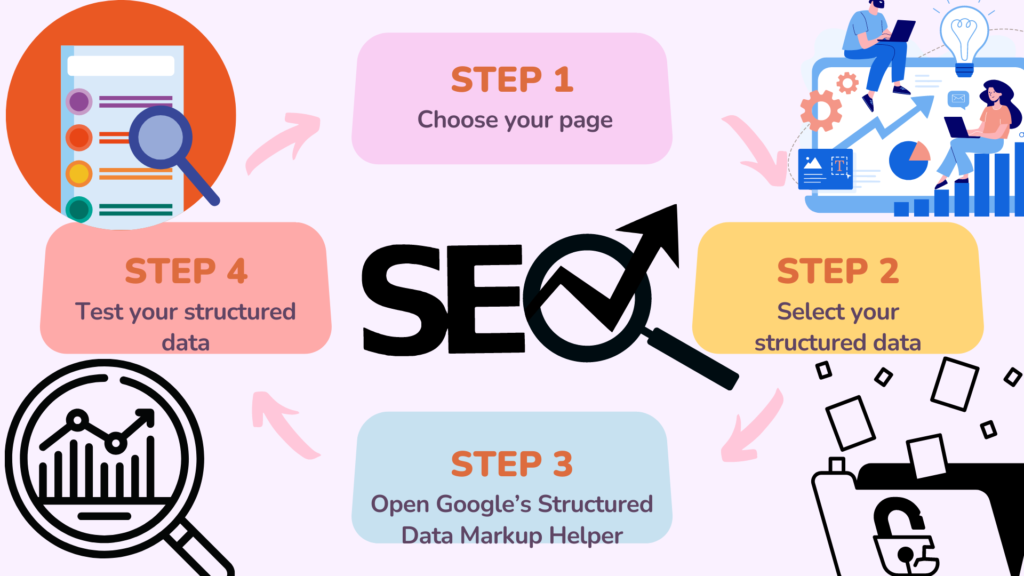
Choose your page
You must first identify which pages will benefit from this before proceeding. For example, if you have a how-to article on cleaning gutters, you can use the how-to schema markup on that page.
In contrast, if you have a blog post that summarizes all of your company’s recent events, you can omit adding any data to it.
You may have dozens of pages or only a handful, depending on your website.
In any case, you’ll want to keep a record of your data efforts, particularly when it comes to replacing older sites.
Making a document in Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets could assist. For example, you may include the URL, the schema markup added, and the date changed.
Select your structured data
The next step is to select your data. Steps one and two of this method may overlap in some circumstances.
You can choose the type of schema markup when you compile pages, for example. you wish to employ Pick the method that works best for you and your team.
Open Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
You can start coding once you’ve chosen your pages and data. This process is made a little easier with Google’s Data Markup Helper tool.
This free application can also be used to leverage this in email correspondence, such as for travel or hotel confirmations.
Test your structured data
Testing is an essential component. If you format or duplicate your data incorrectly, Google will have a hard time understanding it.
Leaving Google perplexed might lead to a drop in ranking, reducing organic traffic and resulting in incorrect snippet information in search results.
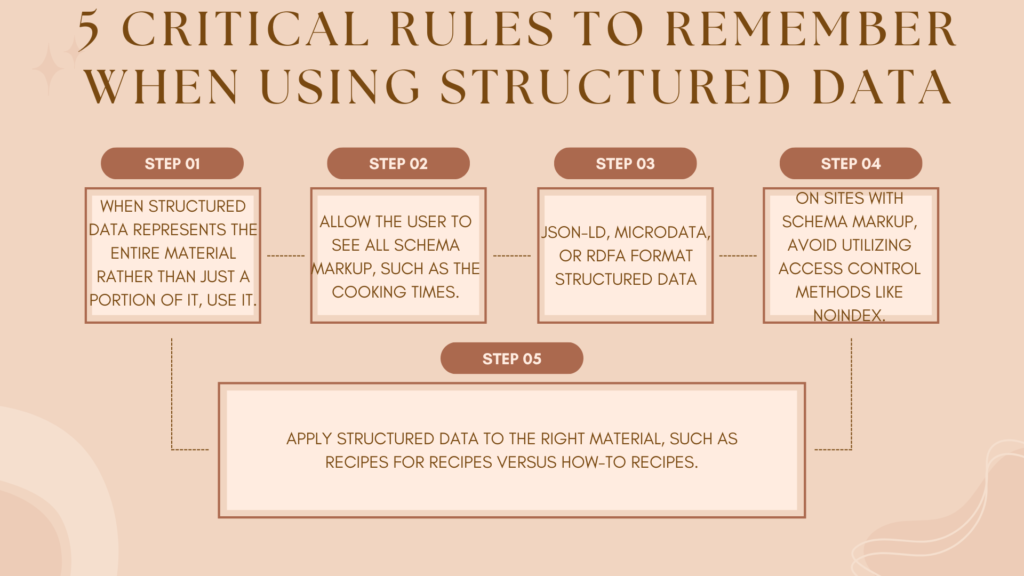
5 critical rules to remember when using structured data
Remember these five rules for the greatest outcomes with this for SEO:
What are the types of structured data for Google search results?
You can choose from a variety of sorts if you chose to use it, including:
- Carousel
- Corporate contact
- Course
- Breadcrumb
- Book
- Article
- Critic review
- Dataset
- Event
- Aggregate rating
- Fact check
- FAQ
- How-to
- Job posting
- And more
5 structured data examples that even beginners can use
It’s great to have some samples for inspiration if you’re new to schema markup.
Take a look at these five:
Corporate contact
Your organization can include vital information about itself with the corporate contact data snippet. You can give users rapid access to the data and links they want on your website and social media profiles.
Product
The product data snippet allows your business to communicate important information to customers. Using schema markup on all of your product pages, you can highlight product pricing, reviews, availability, and more.
Sitelinks search box
Your business may make it even easier for users to find what they need on your site with the sitelinks search box data snippet. This type of data can also benefit your SEO strategy by offering useful keyword information.
Video
The video data snippet can take up important real estate in search results, allowing you to steal visitors from your competition. This schema markup also provides rapid solutions to complicated issues, such as how to empty a vacuum cleaner, clean a gutter, or change computer settings.
Events
Your firm can use the events data snippet to highlight future events. Local businesses can benefit greatly from data snippets like this. With this schema markup, you can be front-and-center in search results whether you’re holding a sale, a speaker, or a class.
Structured data tools
A variety of technologies are available to assist you in implementing this. Some of the most trustworthy are provided by the search engines themselves. Among them are:
- Google’s structured data markup helper: Using a step-by-step method, create markup.
- Google’s Rich Results Test: Confirm which rich results your website can generate.
- Schema.org’s Markup Validator: Validate data from Schema.org in your web pages.
- Google’s AMP testing tool: Validate the AMP pages you’ve created.
- Bing’s guide to structured data: Find out how Bing handles data.
- Yandex structured data validator: Use this tool to test your markup if a portion of your audience uses Yandex.
- Facebook’s open graph debugger: Facebook’s open graph markup validator.
Other tools can assist you in completing data-related activities. Among them are:
- Yoast WordPress plugin: Auto-generates certain types of this data for you, such as FAQ and how-to content.
- Keyword research tools: Most feature a SERP analysis that indicates how you rank for data types.
- SEO crawlers: DeepCrawl and Screaming Frog provide this data insights into your own and competitors’ websites.
What Is Unstructured Data?
It is undefined information with no predetermined format. For a long time, Google and other search engines have been analyzing this data, sending bots to scan your website and construct a picture of what it’s about. They are improving all the time, but this data remains a challenge.
Key Differences Between Structured and Unstructured Data
The distinction between structured and unstructured data isn’t limited to SEO. Every type of data is affected by this distinction.
Your contacts, for example, are data (names and numbers are categorized into certain fields), whereas images (assuming they don’t have time or location tags) are considered unstructured data.
- Defined vs. undefined
Structured data fits into predetermined models and formats, making it easier for other applications to comprehend. There is no specified model for unstructured data. In SEO, we employ the Schema.org model to read structured data, which helps all search engines better understand the data on a web page.
- Qualitative vs. quantitative
Unstructured data is often qualitative—interactions on social media, interviews, photographs, and so on. Structured data is more quantifiable, with predetermined fields and quantities.
- Differences in storage
Unstructured data can be quite complicated, necessitating a large amount of storage space (think about the images on your site). Data lakes are used to store unstructured data, whereas data warehouses are used to store structured data, which is much easier to store.
- Ease of analysis
Structured data is significantly easier to evaluate since it fits into predetermined models and forms. This data tells search engines what a piece of information is about, making it easier to understand and deliver to the public.
Semi structured data
It is a hybrid of structured and unstructured information. This is data that, like HTML, does not have a strict structure and instead relies on tags, attributes, and metadata to transmit information fast.
The majority of what we create on the internet is unstructured in and of itself. When you combine unstructured data with a mechanism to organize or find it — such as metadata on web pages or attributes on links — you get semi data.
Conclusion
In SEO, the way you organize information is crucial. It can assist you in making it as simple as possible for search engines to understand what you’re talking about.
The schema format is used to organize data in SEO, and several tools can assist you in efficiently using this “language.”
If you do, your website will appear in rich results, catching the attention of searchers and attracting people to your site. It may seem insignificant, yet it can have a significant impact on the success of your website.

Q- What kinds of structured data are there?
A- JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa are the most common data markup formats supported by Schema.org.
Q- What is the best place to store structured data?
A- JSON-LD should be contained within a script> element in the page’s head or body.
Q- When should structured data be used?
A- It is a technique for providing Google with extensive information about a web page. Google can then use this data to generate rich, informative results. These rich tidbits are popular with viewers.
Q- Is structured data beneficial to your SEO efforts?
A- It aids Google’s understanding of your page, which is beneficial to SEO. Although it isn’t a ranking factor, it does assist Google in displaying your data in its rich results.
Q- What is the significance of structured data?
A- Higher click-through rates, more search visibility, faster indexing, and voice search dominance are all advantages of this. It aids Google’s understanding of your content and can improve your site’s visibility in search results.






