WiFi – Wireless Fidelity Meaning

- Wireless Fidelity Meaning
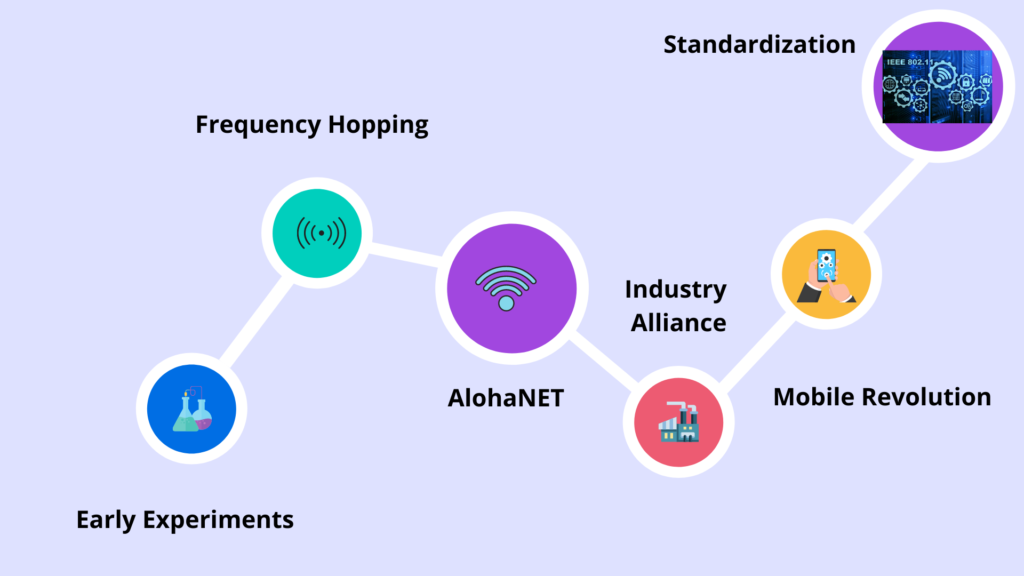
- The origin Of WiFi
- Usage and Application of WiFi
- Advantages and Disadvantages of WiFi
Wireless Fidelity is another name for WiFi. We’re all familiar with WiFi, which can be found on our phones, laptops, and everywhere else that WiFi is supported.
WiFi is a wireless networking technology that allows you to connect to a network or another computer or mobile device without using wires. WiFi uses a circular radio frequency spectrum to deliver data.
WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) is a general word for a wireless network in the communication standard.
WiFi functions similarly to a local area network, but without the usage of wires or connections. The term WLAN relates to a wireless local area network.
IEEE 802.11 is the communication standard. The Physical Data Link Layer (PDLL) is used to operate WiFi. Wi-Fi is built into modern computer devices such as laptops and smartphones, as well as digital cameras and smart TVs.
The origin Of WiFi
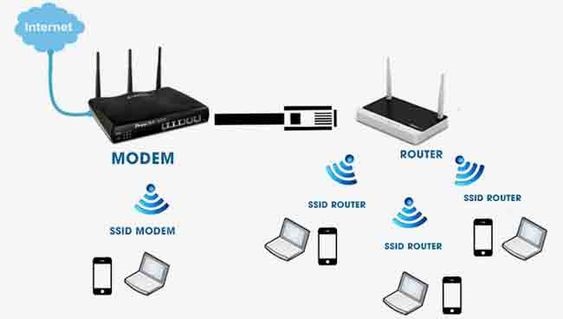
Within a specific range, the access point or base station to client connection, or any client-to-client link.
The router, which provides radio frequency via WiFi, is responsible for the range.
These frequencies now operate on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bandwidths.
All modern laptops and mobile devices are capable of accessing both bandwidths because the WiFi adapter inside the device is responsible for receiving the WiFi signal.
The default bandwidth for all devices is 2.4 GHz.
The Radio Spectrum
WiFi uses the radio spectrum to operate. The radio spectrum includes frequencies ranging from 3 Hz to 3,000 GHz and is portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio waves released within this frequency range are widely used, particularly in communications, rendering them susceptible to interference at various frequencies.
As a result, national laws in conjunction with the International Telecommunication Union govern the generation and transmission of radio waves (ITU).
Usage and Application of WiFi
Wi-Fi has a wide range of uses, including in all areas where computers or digital media are used. Wi-Fi can be utilized for entertainment purposes as well.
The following applications are provided as examples:
- Every day, we utilize Wi-Fi. We can connect to the internet using Wi-Fi from any Wi-Fi-enabled device. Wi-Fi enables us to communicate wirelessly, including streaming and casting audio and video to any device.
- When using Wi-Fi to share files, data, and other items between two or more computers or mobile phones, data transmission speeds are also quite fast.
- A Wi-Fi printer’s capacity to print any document is another significant feature.
- Wi-Fi can also be utilized as a HOTSPOT, giving a localized area wireless Internet access.
- Consumers of Wi-Fi-enabled devices can access the primary network connection via Hotspot while the main network connection is operational, providing them with temporary internet connectivity.
- Wi-Fi adapters use the owner’s network connection to broadcast radio waves and create a hotspot.
- Wi-Fi or WLAN technology can also be used to establish a Point-to-Point network.
- This method can connect two places that are difficult to reach by wire, such as two corporate office buildings.
- Another useful tool is VoWi-Fi, which is also known as voice-over Wi-Fi. A few years ago, telecom companies proposed the Volte (Voice over LTE) standard (Voice over Long-Term Evolution ).
- VoWi-Fi has grown in popularity in recent years, allowing us to make calls to anyone on our home Wi-Fi network.
- The only need is that our phone be linked to the internet via Wi-Fi. Voice is sent over Wi-Fi rather than the mobile SIM network, resulting in excellent voice quality.
- A considerable number of mobile phones already support VoWiFi.
- Wi-Fi Internet access in offices: All computer systems in offices are connected to the Internet via Wi-Fi. There is no need for elaborate wiring in the case of Wi-Fi.
- The network is also really fast. An whole Wi-Fi project, such as a spreadsheet or ppt, can be presented to all participants at once.
- A Wi-Fi cable break does not result in the loss of network connectivity as a cable break would. A city can also provide network connectivity utilizing W-Fi by placing routers at selected areas.
- Schools, colleges, and universities have already implemented Wi-Fi networks due to their flexibility. Wi-Fi can be used as a location system to recognize a device’s region by detecting Wi-Fi deployments.
Types or Kinds of Wifi
As previously said, Wi-Fi comes in a variety of forms or standards. The names of the standards are defined in this section.
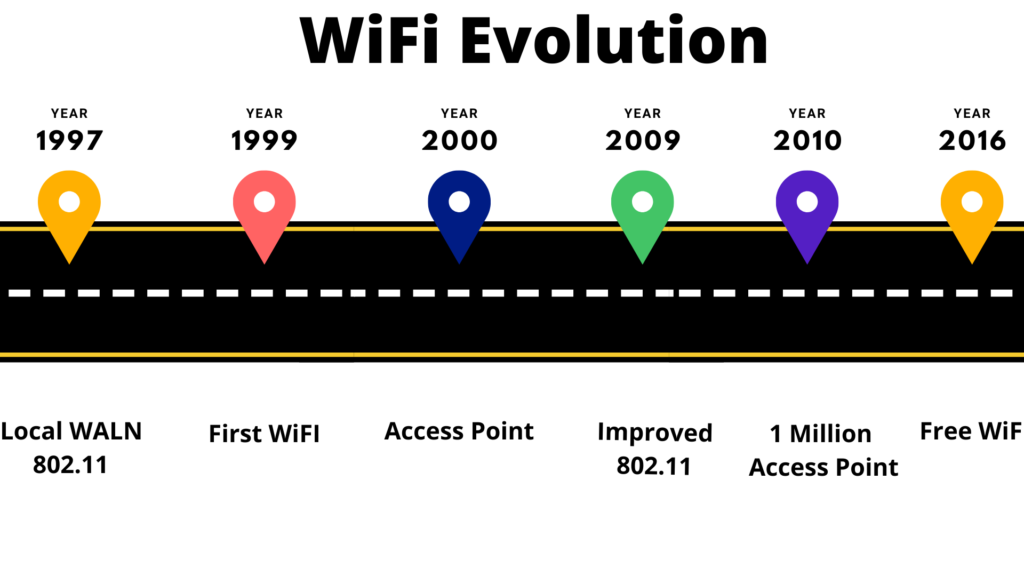
- Wi-Fi-1 (802.11b, launched in 1999) – This version supports link speeds ranging from 2 to 11 megabits per second over the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum.
- In 1999, Wi-Fi-2 (802.11a) was introduced – After a month, the previous version, 802.11a, was introduced, with a link speed of up to 54 Mb/s over the 5 GHz band.
- In 2003, Wi-Fi-3 (802.11g) was introduced – Over 2.4 GHz, the speed was increased to 54 to 108 Mb/s in this edition.
- 802.11i was introduced in 2004 -This is the same as 802.11g, except only the security aspect has been improved.
- 802.11e was introduced in 2004 – This is the same as 802.11g, with the exception of Voice over Wireless LAN and multimedia streaming.
- In 2009, Wi-Fi-4 (802.11n) was introduced– This version supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wireless frequencies, with speeds ranging from 72 to 600 Mb/s.
- In 2014, Wi-Fi-5 (802.11ac) was introduced– In the 5 GHz bands, it supports a speed of 1733 Mb/s.
Huawei introduced 802.11ax, the newest technology of Wi-Fi that can enable 3.5 Gb/s, in 2020.
Read Also:
Working or Functioning of Wifi
What is the Wi-Fi protocol?
First and foremost, Wi-Fi is a wireless communication system that uses electromagnetic waves to transfer networks. Because we know that there are many forms of electromagnetic waves based on their frequency, such as X-rays, Gamma-rays, radio waves, microwaves, and so on, radiofrequency is used in Wi-Fi.
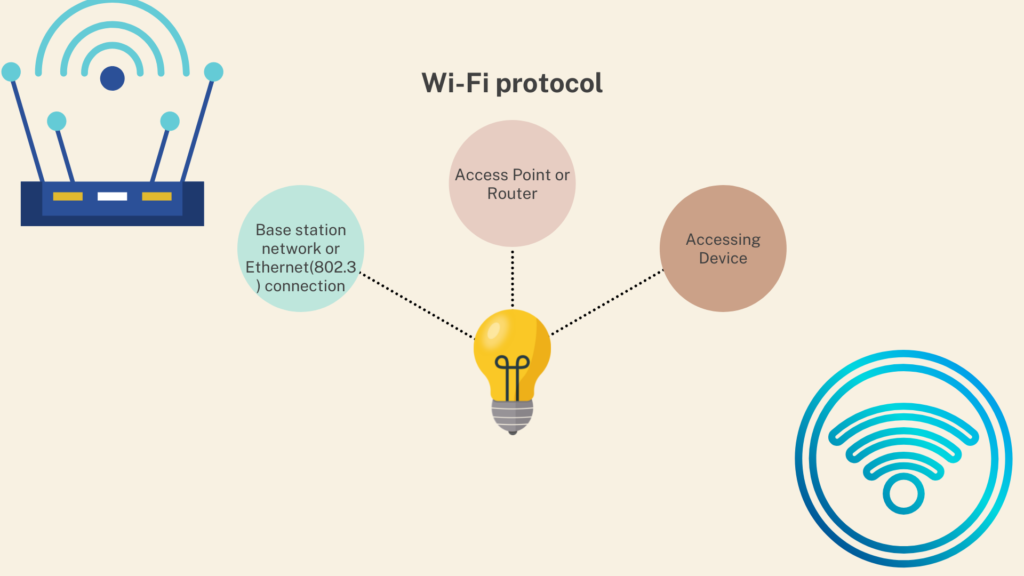
Furthermore, routers and our gadgets read binary data. In this situation, routers send radio waves to our devices, which they obtain and read in binary form. We’ve all seen the binary representation of a wave, in which the highest pick is 1 and the bottom pick is 0.
Terminology of WIFI
Wi-Fi is sometimes known as “wireless LAN.”
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
The service set identification (SSID) numbers, which are 32 characters long, are used to identify and distinguish WiFi networks. Every device is attempting to communicate with the same SSID (Service Set Identifier). The wireless network’s title is called SSID, which stands for “Service Set Identifier.”
WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access- Pre-Shared Key)
It’s a Wi-Fi Alliance Authority initiative that uses Pre-Shared Key authentication to secure wireless networks. WPA is available in three flavors: WPA, WPA2, and WPA3. Unwanted users are kept out of Wi-Fi connections via encryption.
Ad hoc networks
Wi-Fi relies on them to convey data. A wireless mesh network is a point-to-point network without an interface.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WiFi
| Advantages of WiFi | Disadvantages of WiFi |
| Installation does not require complicated wiring and has a diverse network connection. | When utilizing Wi-Fi, mobile phones, computers, and other devices with batteries use a lot of electricity. |
| It is accessible from anywhere inside the Wi-Fi range. | Security vulnerabilities might exist even when encryption is in place. |
| Regulatory permission is not necessary for independent users. | The same manner that recognized devices become unrecognized to the router, Wi-Fi can be hacked and accessed. |
| Furthermore, Wi-Fi Extenders allow you to expand your network. | The speed is slower than with a direct cable connection. |
| Setup is simple and quick. | It can hurt people since it emits radiation similar to cell phones. |
| Only the SSID and password must be set up. | Wi-Fi transmissions can be disrupted by thunderstorms, for example. |
| Wi-Fi networks encrypt radio signals using WPA encryption as part of their security procedures. | Unauthorized access to Wi-Fi is feasible due to the lack of a firewall. |
| It is also less expensive. | We won’t be able to access the internet via Wi-Fi if the power goes off because a router is necessary. |
| Another function it provides is hotspots. | —————————————————- |
| Roaming is also possible. | —————————————————- |
Alternatives to Wifi
Several more wireless technologies are available as alternatives to Wi-Fi:
- Bluetooth is an excellent short-range network.
- WiMax and mobile networks are utilized to provide users with long-range wireless internet connections.
- LoRaWAN is a long-range wireless technology with a low data rate.
- One alternative is to reuse existing cables.
- G.hn uses home cables such as telephone and electricity lines.
- There are several wired computer networking protocols that can be used instead of Wi-Fi, including:
- Twisted pair IEEE 802.3ah
Conclusion
We’ve all heard of Wi-Fi, and we have it on our phones and laptops. Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that allows us to connect to other computers or mobile devices across a wireless network. Data is delivered in a circular range over radio frequencies in Wi-Fi.

Q- What is the significance of the term “wireless fidelity”?
A- Wireless fidelity is a combination of the phrases wireless and fidelity. Wireless denotes the absence of cables or wires for signal transmission, while fidelity denotes long-term support. Wireless Fidelity is defined as a data technology that allows consumers to connect to high-speed internet without the use of cables.
Q- What is the process of wireless fidelity?
A- The establishment of a Wireless Local Area Network is possible because to wireless fidelity. Wireless fidelity, like other wireless technologies, works by transferring signals between devices using radio signals at specific frequencies. Wi-Fi uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Q- Who invented wireless internet?
A- Wi-Fi is credited to Vic Hayes, the leader of the IEEE Committee that established the 802.11 specifications in 1997. He’s even referred to as the “Father of Wi-Fi.” The Wi-Fi Alliance is the organization in charge of commercializing Wi-Fi technology.
Q- What is the distinction between Wi-Fi and wireless?
A- Wireless is a cellular mobile network that allows you to access the internet on your phone without having to install any gear. Wi-Fi, on the other hand, can only be accessed through an installed router. Wireless and Wi-Fi differ in terms of cost, signal range, and data transfer speed.






